What Is Chromium Carbide Overlay Wear Plate and Why Is It More Wear-Resistant Than Regular Steel?
In heavy industries such as mining, cement, and power generation, equipment wear is a significant challenge. Regular steel components often suffer from rapid abrasion, resulting in frequent downtime and costly repairs. This is where chromium carbide overlay wear plate becomes a game-changer. But what makes it significantly more wear-resistant than ordinary steel?
Understanding Chromium Carbide Overlay Wear Plate
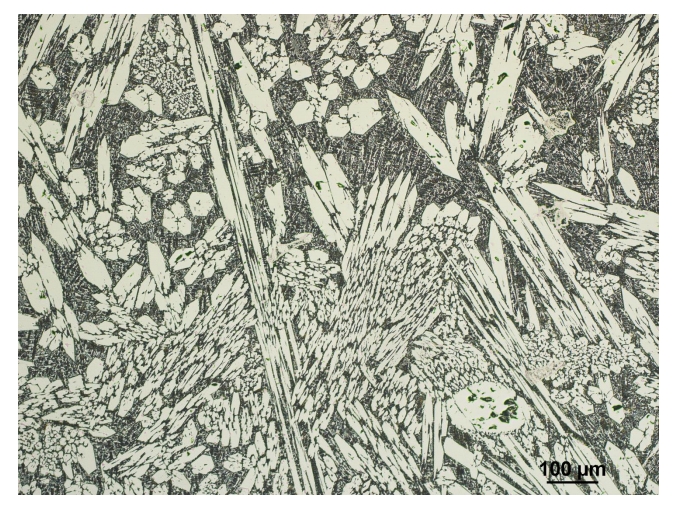
A chromium carbide overlay wear plate is a specialized material designed to resist extreme wear in abrasive environments. It consists of a low-carbon steel base overlaid with a hardfaced layer rich in chromium carbide particles, primarily Cr₇C₃. These carbides form during the welding process and are uniformly distributed across the surface, providing exceptional protection against sliding wear, impact, and erosion.
Unlike standard steel plates, which rely solely on the toughness of the base metal, these plates utilize hard alloy phases embedded in the matrix, greatly extending service life.
Why It Outperforms Regular Steel
1. Superior Carbide Structure
The key to wear resistance lies in the type and distribution of carbides. Regular steel contains iron-based carbides like Fe₃C, which are relatively soft and easily worn down. In contrast, chromium carbide overlay wear plates form high-chromium carbides such as Cr₇C₃ — compounds that exhibit hardness levels of HRC 58–65.
These carbides have excellent stability and abrasion resistance, especially under dry sliding or high-temperature conditions.
Fun Fact: The higher the atomic ratio of chromium to carbon, the more stable and harder the carbides — a primary factor in outperforming conventional wear resistant steel plate.
2. Optimized Microstructure
In quality wear plates, the hardfaced overlay features a martensitic matrix interspersed with a high volume of uniformly distributed carbides. This composite structure allows the plate to resist both sliding abrasion and moderate impact, making it highly versatile.
However, if carbides form unevenly — like in net-like structures or along grain boundaries — wear resistance can decrease sharply. That’s why processing and control are critical.
3. Tough Backing for Welding & Fabrication
Unlike brittle ceramics or tool steel, composite wear plates feature a mild steel base that allows easy welding, bending, and cutting — including plasma and laser cutting. This enables manufacturers to produce complex shapes like curved liners, wear strips, and structural components for custom installations.
Real-World Applications: Where Are These Plates Used?
The chromium carbide clad wear plate is widely used in sectors where high wear is a daily reality:
Mining: Transfer chutes, hoppers, screen plates
Cement plants: Separator cones, clinker feeders, screw conveyors
Thermal power plants: Coal mill liners, ash handling systems
Steel mills: Sinter plants, material bins, discharge chutes
In each case, replacing standard components with a high chromium wear plate drastically extends lifespan and reduces unscheduled maintenance.
Choosing the Right Wear Plate
When selecting a chromium carbide overlay wear plate, consider:
Overlay thickness & composition (e.g., 4+4mm, 6+6mm, 8+6mm)
Carbide volume fraction (30%+ is preferred)
Welding process (submerged arc vs. open arc)
Cutting requirements (plasma, laser)
Also, always verify if the product meets quality benchmarks like hardness uniformity, metallographic structure, and impact resistance.
Post time: Jul-09-2025